A Guide To Research and Development Accounting
In the U.S., the terms of any agreement relating to contracted R&D services must be disclosed in company statements—as must payments received for services and costs incurred. For the purposes of accounting, „research“ can be defined as planned activity that sets out to uncover new knowledge, with the aim of significantly improving existing products or processes, or creating new ones. „Development“ is the activity needed to turn this research into the new or improved product or process.
Governments do so in order to expand general knowledge, meet the goals of society, or develop new military applications. Research and development (R&D) is investigative efforts conducted in order to discover new knowledge that can be applied to practical applications. The amount of R&D spending is usually a relatively low proportion of the total expenditures by any of the preceding organizations. For example, R&D spending is high in the technology industry and low in the shipping industry. Research and development accounting provides information about how much money should be set aside from profit for future activities of R&D by a company. Treat the invoiced costs of any external services provided for the R&D project as incurred expenses.
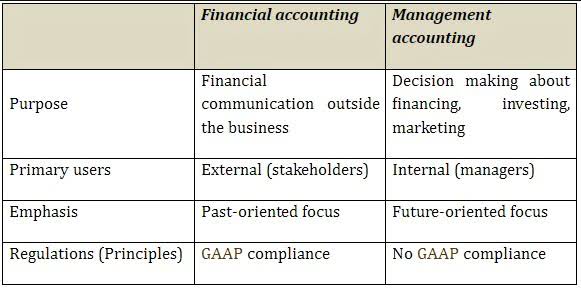
Financial Accounting
R&D costs fall into the category of internally-generated intangible assets, and are therefore subject to specific recognition criteria under both the UK and international standards. Many businesses in the commercial world spend vast amounts of money, on an annual basis, on the research and development of products and services. These entities do this with the intention of developing a product or service that will, in future periods, provide significant amounts of income for years to come. There may be research and development arrangements where a third party (a sponsor) provides funding for the research and development activities of a business.
This is a brief outline of the requirements for accounting for research and development. If you would like to discuss the accounting needs for your R&D project, our team of experienced small business accountants will be glad to help. The government’s Research and Development Expenditure Credit (RDEC) scheme is aimed at small businesses and start-ups that are not liable to corporation tax.
Chapter 8: Research & Development
Company A will need some visibility into Company B’s pattern of performance in order to properly expense the contract research costs under the arrangement based upon the level of effort necessary to perform the research services. The timing of the payment does not alter the timing of the expense recognition. Company A should expense the $3 million when incurred (normally when paid) as research and development costs since the technology has no alternative future uses. GAAP and IFRS is not a question of right or wrong but rather an example of different theories colliding. GAAP prefers not to address the uncertainty inherent in research and development programs but rather to focus on comparability of amounts spent (between years and between companies). GAAP to recognize assets when future benefits are clearly present as a reporting flaw that should not be allowed.
- By calculating these costs accurately, teams can gain valuable insights into their projects’ progress and make better decisions about resource allocation.
- The core accounting rule in this area is that expenditures be charged to expense as incurred.
- Company A has appointed Company B, an independent third party, to develop an existing compound owned by Company A on its behalf.
- Start with a free account to explore 20+ always-free courses and hundreds of finance templates and cheat sheets.
- Note that if an accounting policy of capitalisation is adopted it should be applied consistently to all development projects that meet that criteria.
- It achieves this by adding improvements to the current goods and services or introducing a new product offering.
These arrangements are frequently constructed as limited partnerships, where a related party fulfills the role of general partner. The general partner may be authorized to obtain additional funding by selling limited-partner interests, or extending loans or advances to the partnership that may be repaid from future royalties. The professional guidelines for recording R&D research and development accounting costs were designed with the accrual accounting method in mind. Companies using the cash basis method of accounting will record expenses arising from R&D when they are paid. There are many things companies can do in order to advance in their industries and the overall market. Research and development is just one way they can set themselves apart from their competition.
9 Capitalization of interest incurred on loans received to fund research and development
The key assumptions are that a total of $100,000 has been spent on research and development, there is a $20,000 residual value, the product developed has a commercial life of 5 years, and the amortization expense uses the straight-line method. For government-sponsored research and development grants, the AICPA industry guide, Audits of Federal Government Contractors, addresses the accounting for certain best-efforts research and development cost-sharing arrangements. It is a systematic study that intends to gain a deeper understanding of the fundamental elements of a concept or phenomenon. However, it does not provide the possible applications of concepts or phenomena in production.
Receive timely updates on accounting and financial reporting topics from KPMG. PwC refers to the US member firm or one of its subsidiaries or affiliates, and may sometimes refer to the PwC network. This content is for general information purposes only, and should not be used as a substitute for consultation with professional advisors. A company that focuses on development and buys in research can treat the cost of that research as expenses, together with the cost of any activity needed to make it into a commercial concern. Given the rapid rate of technological advancement, R&D is important for companies to stay competitive.
